Evolution Is Lethal Antiscience
© Joseph Mastropaolo, Ph.D.* Peer reviewed
paper published in Creation Research Society Quarterly 38: 151-158,
2001.[*Professor Emeritus,
California State University, Long Beach; Adjunct Professor of Physiology,
Graduate School, Institute for Creation Research, 10946 Woodside
Avenue N., Santee, CA 92071]
Abstract
The foundation of evolution is abiogenesis, life spontaneously generated
from nonlife. The superstructure placed upon that foundation is monogenesis,
myriad spontaneously generated structures to produce every kind of
simple life form then by countless spontaneous generations every
kind of complex life form. The other “definitions” of
evolution are change over time, common descent and natural selection.
Laboratory abiogenesis has failed consistently and dredging the bottoms
of the oceans yielded the inert sulfate of lime, not the fraudulent “monera.” The
simulated abiogenesis of the proteins to mock-up the simplest original
cell is more than a zillion (>104,000,0000, 1 followed by more
than 4,000,000 zeros) times more impossible than the mathematical
definition of impossible. The probability of monogenesis was not
attempted because myriad multiplications of impossible yield impossible
to unimaginable extremes. The common textbook instructions, “life
arose in the ancient seas” from “that original organic
soup,” are teaching the innumerable miracles of the evolution
religion and that violates the U.S. Constitution’s prohibition
of a state supported church. To meet the requirements of science
and the Constitution, these lessons must be changed to “life
was created,” as in “Henry Ford created the Ford automobile.”
“Change over time,” “definition one” of evolution, actually
describes devolution to extinction, the exact opposite of evolution. “Common
descent,” “definition two” of evolution, actually describes
true-to-type devolution to extinction, again the exact opposite of evolution.
A sample engineering analogue, as well as actual epidemiological data from human
genetic disorders and fatal birth defects, identify “natural selection,” the
alleged “primary mechanism” for evolution, as actually a mechanism
for devolution to extinction, the exact opposite of evolution. Both “definitions” of
evolution and evolution’s “primary mechanism” yield universal
devolution to extinction. Additionally, evolution is the antithesis of science
because it cloaks current permanent accelerating human and biosphere extinction
in the garb of biologically advantageous progress. Evolution wantonly militates
against countermeasures while myriad individuals and populations, including humans,
are accelerated to the greatest mass extinction in history. Therefore, evolution
is identified here as the wantonly lethal antiscience ruling the summit of criminality.
As a first step for self defense against imminent permanent human and biosphere
mass extinction, the evolution movement must be expunged worldwide.
Key words: evolution, creation, lethal, antiscience, abiogenesis, monogenesis,
genetic disorders, extinction, summit criminality, state religion, fatal birth
defects.
I. Introduction
Evolution has ruled biology for more than a century. That is a remarkable
achievement and the purpose of this paper is to illumine why evolution
is so controversial and why it is considered here to be at the
summit of criminality. The approach is to pursue the various definitions
of evolution and to examine the evidence. As needed, principles
from the sciences shall be brought to bear.
The foundation of evolution is abiogenesis, a living cell allegedly springing
to life from nonliving matter. This apparently is based on the “monera” fraud
of Ernst Haeckel (Assmuth and Hull, 1915, pp. 74-76). The nonexistent monera
were misrepresented as primitive missing-link single cells found in the slime
at the bottom of oceans but in fact were inert precipitates of sulfate of lime
(Rupke, 1971, pp. 169-183; Becker, 1999, pp. 14-18). To synthesize a monera,
the Miller-Urey experiments failed remarkably and consistently (Yockey, 1992,
pp. 231, 232, 234, 238 -241; Miller and Levine, 2000, p. 344). Furthermore,
the simulated evolution of a small protein for a small cell yielded an improbability
comparable to a successful perpetual motion machine (Yockey, 1992, p. 257).
In spite of no evidence from nature or the laboratory or simulation, abiogenesis
persists in current high school and university biology textbooks as “life
arose in the ancient seas” from “that original organic soup” (Johnson,
1998, p. 195; Miller and Levine, 2000, pp. 344, 346). To the apparent impossibility
of abiogenesis, evolution concatenates the apparent impossibilities of monogenesis,
the parent cell spontaneously diversifying to form all other kinds of single-cell
organisms, then these in turn spontaneously complicating to all multicellular
life forms.
Another approach to evolution is by way of its meanings. Apparently, there
are three. “Definition one” is change over time. It is stated that
evolution of this type is a fact. “Definition two” is common descent.
This is treated as though it were a fact. “Definition three” is
natural selection, the primary mechanism for definitions one and two (American
Scientific Affiliation, 1996, p. 3).
This study will be limited to an examination of abiogenesis, monogenesis, change
over time, common descent and natural selection.
II. Data On Abiogenesis and Monogenesis
Let us begin by examining the foundation of evolution, abiogenesis. The necessary
elements in nature are believed to have spontaneously joined together and spontaneously
generated life in a cell. We incompletely know, but the cell would not know
at all, that its metabolic functions of digestion, circulation, respiration,
excretion, movement, repair, and reproduction would depend upon the spontaneously
generated polysaccharides, lipids, amino acids, alpha helixes, polypeptide
chains, assembled quaternary protein subunits, and nucleotides. At least all
of these extremely complex subunits must spontaneously self-combine then further
spontaneously combine into the still more complex functioning cellular structures,
like the mazes of conduits containing automatically moving raw materials and
finished products to and from peripheral assembly organelles, energy systems,
long-chain proteins, and nucleic acids. In preparation for an electrical storm,
for example, exactly the right mix of the spontaneously generated DNA, mRNA,
ribosomes, cell membrane material with its millions of gate-controlled apertures,
enzymes, and scores of other protein structures, each a complex machine in
its own right, must be spontaneously and precisely positioned (Behe, 1996,
pp. 262-268; Denton, 1986, p. 263). Then with every atom in the right place
at the right time the first cell might be thunderbolted together and spring
to life. Even these incomplete details are not mentioned in the biology textbooks
and none of the above references are cited. No calculation of the probability
of any of those events is given to the student to estimate whether or not what
is being taught has the same or greater improbability of miracles, which would
rule it out of science. Without evidence, the student is expected to believe
on faith the dogma that a cell somehow sprang to life in the distant past “in
the ancient seas” “that original organic soup” (Johnson,
1998, p.195; Miller and Levine, 2000, p. 346).
The objective determination of abiogenesis as science, or as miracles, may
be approached by observing that many functions in a living cell are determined
by the structures of its proteins. The trail of the first cell therefore leads
us to the peculiar organic chemistry of biologically useful amino acids in
viable proteins. When amino acids are synthesized in the laboratory, about
half are left-handed and about half are right-handed. Yet, only the left-handed
ones are biologically useful. Of the left-handed, there are 20 eligible amino
acids for each of perhaps hundreds of positions in a viable protein, but almost
always only one correct choice can meet the functional requirements. Almost
always a peptide bond is required and any other will cause the protein to fail
biologically. Sometimes with a correct primary structure, the correct secondary
or tertiary or quaternary structures may not materialize because the solution
conditions for the synthesis were not exact. Taking the complex biochemistry
into account which yields the complex submicroscopic geometries biologically
required, a search may be made for the probability of creating a protein by
chance as specified by evolution. Accordingly, the probability of evolving
one molecule of iso-1-cytochrome c, a small protein common in plants and animals,
is an astounding one chance in 2.3 times a trillion vigintillion. A trillion
vigintillion has 75 zeros. In evolution’s terms, if a random mutation
is provided every second from the alleged birth of the universe, then to date
that protein molecule would be only 43% of the way to completion. That is devastating
for evolution because there would be no time to complete that single molecule,
no time to evolve the scores of thousands of proteins required for one cell,
no time to evolve all the other simple cells and no time to evolve all the
complex organisms for a functioning biosphere. The author of this landmark
monograph concluded, “The origin of life by chance in a primeval soup
is impossible in probability in the same way that a perpetual motion machine
is impossible in probability” (Yockey, 1992, pp. 255, 257). That should
settle the question but let us employ an extra measure of patient endurance
and continue the search.
The evolutionist, Richard Dawkins, stated: Suppose we want to suggest, for
instance, that life began when both DNA and its protein- based replication
machinery spontaneously chanced to come into
existence. We can allow ourselves the luxury of such an extravagant theory,
provided that the odds against this coincidence occurring on a planet do not
exceed 100 billion billion to one” (Dawkins, 1996, pp. 144, 146).
The 100 billion billion is 1020. So Dawkins’ own evolutionist criterion
for the impossibility of evolution, one chance in more than 1020, has been
exceeded by more than 50 orders of magnitude not for a whole cell but for only
one molecule of one small protein in that cell. Had Dawkins been influenced
by the literature (Yockey, 1992, pp. 255, 257), he would not have said, “It
is absolutely safe to say that, if you meet somebody who claims not to believe
in evolution, that person is ignorant, stupid or insane (or wicked, but I'd
rather not consider that)” (Johnson, 1993, p.9). Dawkins by his own probability
estimate, with more than 50 orders of magnitude to spare, has identified himself
as a non believer in evolution and needs to ask whether he considers himself “ignorant,
stupid, insane or wicked.” That surfeit of evidence, more than 50 orders
of magnitude, should surely settle the case but let us continue the search.
According to Dembski and Borel, specified events of small probability do not
occur. Dembski estimated 1080 elementary particles in the universe and asked
how many times per second an event could occur. He used the Planck value of
1045. He then calculated the number of seconds from the beginning of the universe
to the present and for good measure multiplied by ten million for 1025 seconds
in all. He thereby obtained 1080 x 1045 x 1025 = 10150, or more exactly 0.5
x 10150, for his Law of Small Probability to eliminate chance (Dembski, 1998,
pp. 5, 62, 209, 210).
Currently, there does not seem to be a scientific criterion more generous to
evolution than Dembski’s one chance in 0.5 x 10150. Anything as rare
as that probability had absolutely no possibility of happening by chance at
any time by any conceivable specifying agent by any conceivable process throughout
all of cosmic history. To test against that criterion, we take one chance in
2.3 x 1075 for one protein (Yockey, 1992, pp. 255, 257) and multiply by the
60,000 proteins required for the abiogenesis of a minimal cell (Denton, 1986,
p. 263; Morowitz, 1966, pp. 446-459) and obtain one chance in more than 104,478,296
(Mastropaolo, 1999, p. iii). That exceeds Dembski’s most generous criterion
for impossible by more than 104,478,146. Or if 0.5 x 10150 to 1 is the most
generous probability science can provide to demarcate possibility from miracle,
then with more than four million orders of magnitude to spare abiogenesis must
be considered miraculous. To put abiogenesis in biology textbooks as evolutionists
have done throughout the United States is to teach evolution religion as science
and that violates the requirement of the U.S. Constitution prohibiting the
establishment of a state religion (Constitution of the United States of America,
1787, Amendment I, see note).
With abiogenesis so unimaginably impossible, it is a waste of time to examine
monogenesis which rests upon the abiogenesis foundation. With the innumerable
spontaneous generations of abiogenesis so impossible, the additional countless
spontaneous generations of monogenesis built upon that foundation are impossible
to an even greater extreme. In order to document this problem of comprehending
such extreme impossibilities, dimensioning the improbability of abiogenesis
may be useful. Numbers like 104,478,296 are incomprehensively large. It is
the number 1 followed by 4,478,296 zeros. There is no English word for it.
There ought to be some way to give a sense of such a magnitude. For example,
if a perpetual motion machine is probabilistically impossible and has a probability
of 1075 to 1 against it (Yockey, 1992, pp. 255, 257), then how many impossible
perpetual motion machines would abiogenesis’ 104,478,296 to 1 against
it represent? The answer is the impossibility of 104,478,221 perpetual motion
machines, also a number too large to imagine. Let us persevere and consider
the Blue Fairy that animated Pinocchio (Collodi, 1883, see note) as one chance
in 10150, that is, she is impossible according to Dembski’s criterion
for impossible. The abiogenesis of only one type of simple unassembled protein
raw material to mock-up a minimal original cell is more impossible than 104,478,146
Blue Fairies. Again, this is too large a number to imagine. In passing, we
may note that evolution is likely the greatest fairy tale ever told because
every elementary particle, like an electron, in the entire cosmos could be
occupied by a Blue Fairy playing Musical Chairs at the incredible tempo of
1045 changes per second for more than 20 billion years with more than 104,478,146
Blue Fairies patiently waiting a turn to play. Instead of biology, American
students are being taught evolution’s peerless blend of championship
science fiction with children’s fairy tales. But let us not give up.
Let us consider a universe 100 billion light years in diameter, probably double
the size of ours, and ask how many trips across that universe we could make
if each probability unit was equal to the diameter of a hydrogen atom. With
the hydrogen atoms side by side, the answer would be 104,478,259 trips, again
too large for the imagination. Abiogenesis is so immensely improbable that
it defies finding a reference to common experience or even a language equivalent
to express it abstractly.
To give a language reference, let us define “zillion” as greater
than 104,000,000 (1 followed by more than 4,000,000 zeros) and let us define “create” as
Webster renders its first meaning, “to cause to come into existence;
bring into being; make; originate; esp., to make or design (something requiring
art, skill, invention, etc.).” We may quite properly say, “Henry
Ford created the Ford automobile,” without attributing to Henry Ford
any divine status. Now let us employ these definitions and properly conclude
that the probability of evolution’s foundation, abiogenesis, and its
superstructure, monogenesis, is more than a zillion to one against them and
the probability of creation, without religious connotation, is more than a
zillion to one in favor of it. Such probabilities remove every vestige of the
vaguest doubt from any objective scientist. Let us close with the reminder
that those probabilities are for only one type of simple unassembled protein
to mock-up the simplest original cell and they represent gross underestimates.
The improbabilities for a complete cell or for a complex life form of trillions
of cells or for an ecosystem of millions of different interdependent complex
life forms would require multiplications by myriad additional orders of magnitude.
The evolutionist mind of Anaximander (611-549 B.C.) must be complimented for
imagining abiogenesis and monogenesis (Durant, 1939, p. 138), concepts so improbable
that human minds are incapable of comprehending the extent of their impossibility.
Authors like Johnson (1998) and Miller and Levine (2000) would be well advised
to discontinue violations of the Constitution by removing from their public
school textbooks all mention of the countless incredible miracles, abiogenesis
and monogenesis. They would bring their public school textbooks into compliance
with the requirements of science and the Constitution of the United States
of America and the Constitution of the State of California if they substituted, “life
was created.”
III. Data On the Three “Definitions” of Evolution
Let us now consider “definition one” of evolution, “change
over time.” “Because such changes have been repeatedly observed,
evolution of this type is a fact” (American Scientific Affiliation, 1996,
p. 3). According to common observation, however, all individuals in the biosphere
age and die. Once dead, the plants rot and the animals putrefy to simpler nonviable
elements. Individually, life forms devolve. Types of life forms as populations
also regress from viable to permanent extinction. That too is devolution, not
evolution. The nonviable universe also devolves (Humphreys 1978). The first
definition of evolution is antonymous to the trillions of consistent observations
of billions of people over thousands of years. The exclusive fact is devolution.
“Definition two” for evolution is common descent. This “view
that all (or most all) life forms, extant and extinct, are related by common
ancestry: a theory about the history of life . . . the common sense observation
that all offspring have parents, have led [sic] many scientists to treat the
inference of common ancestry as though it were a fact” (American Scientific
Affiliation, 1996, p. 3). According to common observation, however, individuals
age and die as the same type of individual at birth. Individuals also reproduce
true to type. Types of life forms as populations demonstrate variability in characteristics
like size, weight, color, and speed of motion but always breed true to their
type. For example, Shetland horses may weigh 300 pounds and Belgian horses may
weigh a ton more than that. Horses may be described by a mean and a standard
deviation for body weight or any other characteristic of horses. It is common
knowledge that all variability in parents and offspring is within their type.
No mare has ever given birth to a calf and no cow has ever born a foal. Life
forms do not transmute to other types of life forms. Life forms as individuals
and populations have been observed devolving to extinction but never evolving.
The second definition of evolution is antonymous to the trillions of consistent
observations of billions of people over thousands of years. Again, devolution
is the exclusive fact.
“Definition three” of evolution is natural selection, “The
theory (acting upon genetic variations, such as mutation) has been the primary
mechanism for the biological changes described in definitions one and two” (American
Scientific Affiliation, 1996, p. 3, emphasis in the original). As documented
above, definitions one and two are definitions of devolution, not evolution.
Also as documented above, the alternative definition of evolution, abiogenesis,
is so impossible it strains the imagination and must be classified as countless
miracles. The superstructure of innumerable spontaneous generations, monogenesis,
is countless multiples more impossible than abiogenesis and also must be classified
as countless additional miracles.
For the sake of discussion, let us consider whether or not genetic variations,
such as mutation, may in any way mitigate those extreme impossibilities. Evolutionists
would have us believe that mutations will yield new and better life forms that
will result in many different kinds of plants and animals, i.e. diversification,
and a progression to higher, more complex life forms. To clarify that logic,
let us select one example from an almost infinite number of thought experiments.
Let us take the circuit board out of an AM radio, put on a blindfold, then
put a finger on the board. To simulate a mutation, if the finger lands on a
connection, break that connection or if the finger lands where there is no
connection, then make one. Reassemble the radio and test its range of stations
for reception. Repeat the process. If the radio increases its range of stations
or improves its reception, then we conclude that mutations cause improved structure
and function. Or if it becomes an FM radio, then the modifications mimicking
random mutations succeeded in producing diversification. If the radio becomes
a TV, then the mutations succeeded in producing the equivalent of an advanced
life form. Contrarily, if the radio progressively degrades to the point of
no longer working, then the mutations produced extinction. Obviously, there
is no chance of obtaining a TV because the AM radio has no monitor and none
of the other special parts and circuits that a TV requires. And like living
things, the AM radio could not spontaneously generate all those special TV
parts because that would violate the laws of physics. Obviously, there is no
chance of obtaining an FM radio because the design, frequency modulation, is
significantly different from an AM, amplitude modulation, radio and cannot
be constructed by introducing mutations into an AM design. Obviously, the radio
will degrade to the point of not working at all and that is consistent with
all human experience. In all human experience, there is no analogous model
to suggest that natural selection and genetic variations, like mutations, will
cause diversity or increased complexity. There is no such experience with life
forms, either. All human experience suggests that all things, especially the
complex, nonviable and viable alike, degrade toward permanent extinction. With
its genetic variations and mutations, natural selection accelerates extinction,
not evolution. Let us next consider human mutations.
Mendelian inheritance in man is “
an encyclopedia of human genes and the disorders and other traits with which
they are associated. It has been in creation and updating for over 35 years
and has been computerized for most of that time. In addition to the print edition
(Figure 1), it has been distributed online (OMIM) since 1987 and by compact
disc (MIM-CDTM) since late 1993.” (McKusick, 1998, Vol. 1, xiii - xviii)
Apparently, this database in the National Center for Biotechnology Information
at Johns Hopkins University is the best in the world for the current catalog
of human genes and genetic disorders.
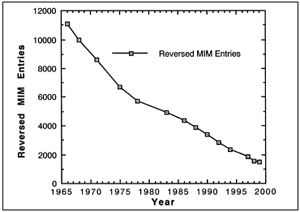 |
| Figure 1. If evolution were true, these would
be the medically reported genetic disorders from 1966 to 1999. These data are actually reversed. Like these data, evolution is false. |
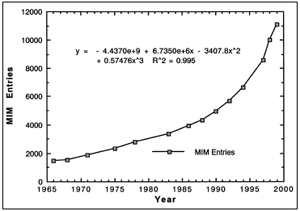 |
| Figure 2. McKusick: Mendelian
Inheritance in Man, Reported Genetic Disorders 1966 to 1999. The number of medically reported genetic disorders in 1966 was 1,487. The number reported by 1999 was 11,099. A curve of best fit has an R2 of 0.995. These data are evidence of devolution. |
Medically reported human genetic disorders have been cataloged in
the above reference since 1966. If evolution were true, then we should
observe a decrease
in genetic disorders over time according to the first definition of evolution,
change over time, and the third definition, natural selection. That means that
the graph would look like the hypothetical Figure 1. The data in Figure 1 are
actually reversed. Like those data, evolution is false. The true data are plotted
in Figure 2. As can be seen, the trend is an exponential increase in medically
reported genetic disorders. Beyond any doubt, the trend is devolution. The
data thereby demonstrate that the ravages of time produce mutations that result
in devolution, the exact opposite of evolution (McKusick, 1998, Vol. 1, xiii
- xviii)
By 2031, it is estimated (R2 = 0.995) there will be 100,000 human
genetic disorders and by 2096 1,000,000 (see Figure 3). “At least one clinical disorder
has been related to 1,318 of the mapped loci (roughly 30%)” (McKusick,
1998, Vol. 1, xiii - xviii). That suggests genetic disorder saturation of
each locus by 2031 and supersaturation by 2096. These data confirm human
devolution
and suggest imminent permanent genetic extinction in this century. That evolution
cloaks imminent human extinction as biological progress, thereby militating
against countermeasures until permanently too late, identifies evolution
as the summit of criminality.
Evolutionists are aware of genetic disorders like the sickle cell allele,
a red blood cell mutation. For example in recent biology textbooks we find, “The
sickle cell allele confers an unexpected advantage in Africa,” (Johnson,
1998, pp. 128, 183) and “Why is sickle cell anemia so common in some
regions . . . The answer to that question is a surprising lesson in evolution
. . . That mutation conferred an advantage wherever malaria was common, and
thus it was favored by natural selection” (Miller and Levine, 2000, p.
233). Evolutionists call it “a classic case of heterozygote superiority” because
survival of heterozygous individuals in malarial regions of West Africa is
1.0 compared to 0.9 for individuals with normal homozygous hemoglobin. They
gloss over the fact that survival for homozygous sickle-cell individuals is
0.2. Also glossed over is that the survival average for normal hemoglobin,
homozygous plus heterozygous with the sickle-cell mutation, is 0.95 compared
to the sickle-cell average of 0.6. Even in malarial environments, normal hemoglobin
permits a survival advantage of at least 35% and of as much as 70% (Hartl and
Clark, 1997, p. 251). In a non-malarial environment, there were 75,000 hospitalizations
per year of 6.1 days with significant mortality. “Thus, sickle cell disease
is one of the most prevalent genetic disorders in the US” (Ashley-Koch,
Yang and Olney, 2000). The evolutionists’ classic case of biological
superiority thus is filling hospitals and graveyards with the afflicted.
The sickle-cell allele is genetic disorder-disease MIM - OMIM number 141,900
and
such disorders have been increasing exponentially (McKusick, 1998, Vol. 1,
xiii - xviii). This demonstrates that evolutionists choose to put at risk
vulnerable students and their families rather than admit that mutations are
genetic disorders
documenting devolution, not evolution. Genetic disorders are reason for alarm
and countermeasures, not wanton misrepresentation. Cloaking significant morbidity
and mortality as biological progress called, evolution, identifies evolution
as lethal antiscience.
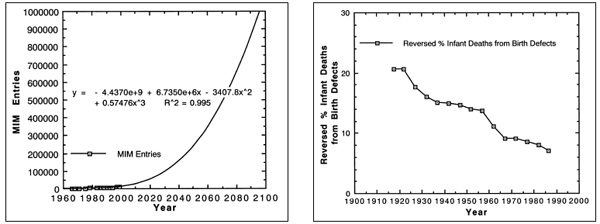 |
|
| Figure 3. McKusick: Mendelian
Inheritance in Man, Reported Genetic Disorders 1966 to 1999 with Extrapolation to the Year 2096. The number of medically reported genetic disorders in 1966 was 1,487, in 1999 11,099. A prediction equation 99.5% accurate suggests 100,000 human genetic disorders by 2031 and 1,000,000 by 2096. These data are evidence of devolution and suggest imminent human extinction. |
Figure 4. If evolution were
true, these would be the percentage
|
In 1997 from genetic testing, the estimate was that everyone on average
carried six genetic disorders (Gargus, 1997). The extrapolation suggests
that by
2033 the average for every man, woman and child may be 60 or more genetic
disorders.
The data indicate that the greatest mass extinction in the history of the
planet is in progress in non human life forms at a rate of 30,000 extinctions
per
year and accelerating (Leakey and Lewin, 1996, Chapter 13; Mass Extinction
References, 1998). The clear message is that mutations accelerate the permanent
extinction of all life forms, including humans. There can be no greater imperative
than educating students and parents to those facts. The lethal masquerade
of portraying mutations as advantageous biological evolution must be extinguished
before it brings the entire biosphere, including all of humanity, to permanent
extinction. Cloaking the greatest mass extinction in the history of our planet
as the biological progress called, evolution, identifies evolution as the
most
lethal antiscience in the history of our planet.
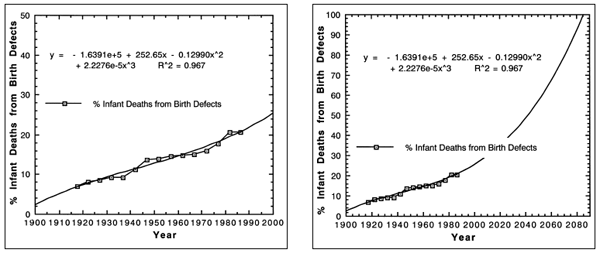
Data on fatal human birth defects may be found in the medical epidemiological
teratology literature. If evolution were true, then we should observe a decrease
in fatal birth defects over time according to the first definition of evolution,
change over time, and the third definition, natural selection. That means
that a graph of the medically reported fatal birth defects should look like
the
hypothetical Figure 4. The data in Figure 4 are actually reversed. Like those
data, evolution is false. The true data are plotted in Figure 5. As can be
seen, the trend in spite of medical advances is an exponential increase in
fatal birth defects (Sever, Lynberg and Edmons, 1993). Beyond any doubt,
the trend is devolution. By 2085, it is estimated (R2 = 0.967) there will
be 100%
human infant deaths attributed to birth defects (see Figure 6). That suggests
that the genetic disorder saturation of each chromosome locus by 2031, and
the supersaturation by 2096, will manifest 100% infant deaths from birth
defects by 2085. These data agree with the genetic disorder data in confirming
human
devolution and in suggesting imminent permanent genetic extinction in this
century. That evolution cloaks accelerating human birth defect mortality
toward imminent human extinction as biological progress, thereby militating
against
countermeasures until permanently too late, adds additional evidence to the
identification of evolution as antiscience at the summit of criminality.
 |
|
|
Figure 5. Percentage of Infant Deaths
Attributed to
|
Figure 6. Percentage of Infant
Deaths Attributed to |
The World War II crimes of the Nürnberg Trials can hardly compare
to the slaughter of all humanity and the entire biosphere. Crimes
against peace, war
crimes and crimes against humanity are minor lapses compared to the extinction
of all life forms. Not just scores of strains of millions of individuals
? surfeit enough in horror beyond imagining ? are at stake, but rather
many millions
of species and many billions of individuals. And if this historically greatest
of all mass bioslaughters currently under way depletes the critical biomass
for sustainable ecobalance, then the universe’s only known biosphere
will erode irreparably to a barrenness as ghostly as the moon. No megacrime
in the history of this planet, or of this universe, comes close to that summit
of criminality.
IV. Summary and Conclusions
According to the most generous mathematical criteria for evolution, abiogenesis
and monogenesis are impossible to unimaginable extremes. The three definitions
of evolution are disguised definitions of devolution to extinction. For the
entire biosphere including all humanity, our planet currently is in the throes
of the greatest mass extinction in its history. The tens of thousands of
different life forms permanently extinguished each year are accelerating
the depletion
of the biosphere to the level where it permanently will no longer support
human life because no new life forms can be created and none can be evolved.
That
evolution cloaks these mass extinctions and the imminent permanent extinction
of all humanity as biologically advantageous is identified here as wanton,
lethal antiscience at the summit of criminality. There can be no greater
imperative for the educational and governmental institutions of the world
than countering
the greatest mass extinction in history as induced over the last 140 years
by the evolution movement. As a first step for self defense against imminent
permanent human and biosphere extinction, the lethal antiscience, evolution,
must be expunged worldwide.
References
CRSQ: Creation Research Society Quarterly American Science Affiliation.
1996. A school board success story. American Science Affiliation
science brief. ASA Newsletter, 38 (1):
1-4.
Ashley-Koch, A., Q.Yang and R.S. Olney. 2000. Hemoglobin S allele and sickle
cell disease. American Journal of Epidemiology 151(9):839-845. Also a Human
Genome Epidemiology (HuGE) Review, 5 August 1998.
Assmuth, J. and Ernest R. Hull. 1915. Haeckel’s frauds and forgeries.
P.J. Kennedy & Sons, New York.
Becker, David R. 1999. The monera fallacy. Watchmaker 6 (2): 14-18.
Behe, Michael J. 1996. Darwin’s black box: the biochemical challenge
to evolution. Touchstone, New York.
Collodi, Carlo (Carlo Lorenzini). 1883. Le avventure di Pinocchio. Felice Paggi
Libraio - Editore, Firenze. Note: The fairy with the turquoise blue hair animated
the wooden marionette, Pinocchio, with the spirit of a boy, then later transferred
that spirit into a spontaneously generated human boy. The discarded marionette
in a corner became lifeless once more without a trace of the role it played
in the abiogeneses of the boy. The parallels with the abiogeneses and the monogeneses
of evolution are striking.
Constitution of the United States of America. 1787. Amendment I, "Restriction
on Powers of Congress [Section 1*.] Congress shall make no law respecting an
establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof;" Ratified
December 15, 1791. Note. This is frequently cited in legal cases as the Establishment
Clause, the prohibition of a state religion, and in Civil Rights cases prohibiting
prejudice against religion.
Dawkins, Richard. 1996. The blind watchmaker: why the evidence of evolution
reveals a universe without design. W.W. Norton & Co., New York.
Dembski, William A. 1998. The design inference:eliminating chance through small
probabilities. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
Denton, Michael. 1986. Evolution: a theory in crisis. Adler&Adler, Bethesda,
Maryland.
Durant, Will. 1939. The story of civilization, the life of Greece. Simon and
Schuster, New York.
Gargus, J. Jay. 1997 “Human genetic research, state of the science.” Session
4, October 13, Faith and science series, St. Elizabeth Ann Seton Catholic Church,
Irvine, California.
Hartl, D.L. and A.G. Clark. 1997. Principles of population genetics. Sinauer
Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA.
Humphreys, D.R. 1978. Using the Second Law more effectively. CRSQ 14: 209-210.
Johnson, G. B. 1998. Biology, visualizing life. Holt, Rinehart and Winston,
Austin, New York, Orlando, Chicago, Atlanta, San Francisco, Boston, Dallas,
Toronto, London.
Johnson, Phillip E. 1993. Darwin on trial. InterVarsity Press, Downers Grove,
Illinois.
Leakey, Richard E. and Roger Lewin. 1996. The sixth extinction : biodiversity
and its survival. Weidenfeld and Nicolson, London.
Mass extinction references. 1998. http://www.well.com/user/davidu/extinction.html#anchor18171.
Mastropaolo, Joseph. 1999. Evolution is biologically impossible. Acts and Facts
28 (11): i-iv, Impact #317. http://www.icr.org/pubs/imp/imp-317.htm. Institute
for Creation Research, El Cahon, CA.
McKusick, V.A. 1998. Mendelian inheritance in man: a catalog of human genes
and genetic disorders. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore.
Miller, Kenneth R. and Joseph Levine. 2000. Biology. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle
River, New Jersey.
Morowitz, H.J. 1966. The minimum size of cells. In Wostenholme, G.E.W. and
M. O’Connor (editors), Principles of biomolecular organization, pp. 446-462.
J.A. Churchill, London.
Rupke, N.A. 1971. A summary of the monera fallacy. In Walter E. Lammerts (editor),
Scientific studies in special creation, pp. 169-183. Presbyterian and Reformed
Publishing Co.
Sever, L., M.C. Lynberg and L.D. Edmons. 1993. The impact of congenital malformations
on public health. Teratology 48 (6): 547-549.
Yockey, Hubert P. 1992. Information theory and molecular biology. Cambridge
University Press, Cambridge, England. Mastropaolo 20 January 2001 #











