Unit 7
Part I: Listen and Learn 4
Click on the speaker icon of the
following sentences and listen to the recording. The Chinese characters
are in big5 format.
-
 Xi
Xi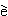 l
l osh
osh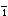 ,
n
,
n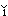 Y
Y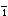 ngy
ngy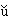 shu
shu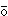 de h
de h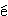 n h
n h o.
o.
Prof. Xie, you speak English very
well.
謝老師﹐你英語說得很好。
-
 N
N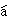 l
l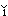 , m
, m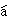 mah
mah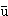 h
h .
.
No, just so-so.
哪裡﹐馬馬虎虎。
-
 N
N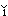 Y
Y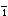 ngy
ngy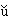 sh
sh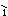 z
z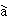 i n
i n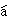 l
l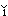 xu
xu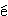 de?
de?
Where did you learn English?
你英語是在哪裡學的﹖
-
 W
W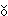 sh
sh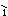 z
z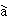 i
Sh
i
Sh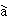 ngh
ngh i xu
i xu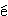 de.
de.
I learned it in Shanghai.
我是在上海學的。
-
 N
N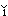 de l
de l osh
osh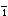 sh
sh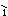 M
M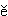 igu
igu r
r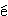 n ba?
n ba?
(I guess) your instructors are Americans.
你的老師是美國人吧﹖
-
 B
B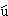 sh
sh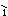 . Y
. Y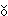 ude
sh
ude
sh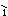 M
M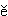 igu
igu r
r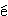 n, y
n, y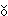 ude sh
ude sh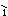 Zh
Zh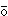 nggu
nggu r
r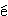 n.
n.
No, some are Americans, some are
Chinese.
不是﹐有的是美國人﹐有的是中國人。
-
 M
M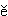 igu
igu l
l osh
osh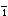 sh
sh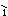 c
c ng n
ng n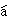 l
l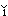 l
l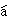 i de?
i de?
Where are American isntructors from?
美國老師是從哪裡來的﹖
-
 Y
Y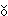 ude sh
ude sh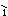 c
c ng
Pittsburgh l
ng
Pittsburgh l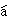 i de, y
i de, y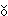 ude
sh
ude
sh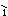 c
c ng Seattle
l
ng Seattle
l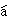 i de.
i de.
Some are from Pittsburgh, some are
from Seattle.
有的是 Pittsburgh 從來的﹐有的是從
Seattle 來的。
 W
W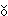 men h
men h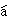 i y
i y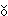 u
c
u
c ng Y
ng Y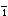 nggu
nggu l
l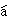 i de l
i de l osh
osh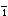 .
.
We also have professors who came
from England.
我們還有從英國來的老師。
Notes:
-
'N
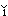 Y
Y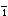 ngy
ngy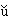 sh
sh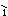 z
z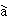 i n
i n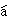 l
l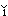 xu
xu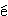 de' means 'Where did you learn...? 'sh
de' means 'Where did you learn...? 'sh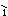 ...de'
construction is often used to indicated what happened when and where. In
the similar way, you can say:
...de'
construction is often used to indicated what happened when and where. In
the similar way, you can say:
'W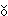 sh
sh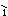 z
z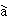 i Sh
i Sh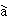 ngh
ngh i
ch
i
ch sh
sh ng de.' (I
was born in Shanghai.)
ng de.' (I
was born in Shanghai.)
'W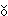 sh
sh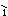 c
c ng Sh
ng Sh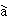 ngh
ngh i
l
i
l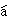 i de.' (I came from Shanghai.)
i de.' (I came from Shanghai.)
-
'Y
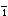 nggu
nggu l
l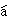 ide l
ide l osh
osh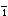 '
- the teachers who came from England. This construction is similar to English
relative clause. In English, the clause is attached to the right of the
noun. In Chinese it is always attached to the left of the noun. This is
an important feature in Chinese.
'
- the teachers who came from England. This construction is similar to English
relative clause. In English, the clause is attached to the right of the
noun. In Chinese it is always attached to the left of the noun. This is
an important feature in Chinese.
[Go back to
Unit 7] [Go to 7-5]
 Xi
Xi N
N N
N W
W N
N B
B M
M Y
Y W
Wmen h
i y
u
c
ng Y
nggu
l
i de l
osh
.