

|
POPULATION
The data for the
population of Japan is incomplete before the period of 1868 . It is believed that
the population of Japan reached 5 million in the 7th century and 10 million
in the 14th century. In 1920 Japan's first census was taken and the
country had a population of 55,963,000. In 1940, Japan's population
reached 73,114,000. Today, Japan is the world's eighth most populous
country. Japan's population climbed over the 100 million mark in
1967, and at the 1990 census it reached 123,612,396. Yet Japan has
one of the world's lowest population growth rates at 0.3 percent per year.
Japan is one of the worlds most densely populated countries. In 1993 the
population density as a whole was about 855 people per square mile, but
if Japan's urban land area is looked at just by itself, the density is several
times greater than it is for the entire country.
The majority of
people live on the coastal lowlands which represents only a small portion of
Japan's total land area. Japan is one of Asia's most urbanized countries.
In 1920 four fifths of the people lived in rural areas and in 1993 about
77 percent of the people lived in cities. In the mountain regions,
only the valleys are populated. The most thinly populated part of Japan is Hokkaido with only 171 inhabitants to the square mile and in the plains areas it is around 3100 inhabitants
per square mile. In Tokyo it is now as high as 15,000 inhabitants
to the square mile. The reason for the people moving closer to the
cities is the higher wages that can be earned there.
ORGANIZATION
Social Structure
The social structure
of Japan consists of 99.5 % Japanese with the balance predominantly Asian minorities who do not stand out from the rest of
the population. The Japanese people are fairly homogeneous, both
culturally and racially. The spoken language is Japanese, and almost
all of the people are of the Mongoloid race. Koreans are the largest alien
group in Japan and number about 688,000. The Ainu are a native people
of northern Japan and have been almost completely assimilated into the
general population. There are also between 2 and 3 million Burakumin.
The term burakumin means 'hamlet people', but this hides their true status
as descendants of outcasts. They were people who engaged in occupations
that were declared ritually unclean, such as gravediggers, butchers, or
leatherworkers. These people are ethnically Japanese, but are often
victims of discrimination because of their low status in society.
Family
The proportion
of young people has been on the decline. The average
family size has also been shrinking, dropping from about five members
in 1955 to about three members per family in 1990. One reason this
drop occurred was because younger married couples were establishing their
own households instead of living with their parents. Another reason
for this drop in family size was that young couples were having fewer children.
In Japan, contraception is not a popular form of birth control but abortion
is a widely used form of birth control.
Culture
For nearly
2,000 years, an intimate relationship existed between Japan and China. For
much of Japan's history, the relationship with China has been that of pupil
to teacher. As early as the 1st century AD, the Japanese visited the Chinese
Imperial court. The Japanese brought back many cultural treasures that
enriched their lives. Some of the cultural treasures were the Buddhist
religion, Confucian ethics, written language, literature, art, architecture,
music, and methods of government. In the late 19th century, the coming
of the Industrial Revolution to Asia changed this relationship. Japan emerged
from more then two centuries of self-imposed isolation. Japan recognized
that this was the only way of gaining equality with the Western powers.
After mastering western techniques, Japan soon built factories and created
a modern army and navy. Even though Japan modernized quickly, there are
still contrasts in the everyday life of the Japanese people. The
major differences are between the more traditional countryside and the
bustling urban centers. Less then 5% of the Japanese people live in small
farming villages and their way of life has changed, but their traditional
patterns established centuries ago can still be observed.
Government
The Meiji
constitution of 1889 was superseded on May 3rd 1947 by the present constitution,
which provided the basis for the development of a democratic society in
Japan. Sovereign power now lies with the Japanese people. Other
important principles under the new constitution are the separation of legislative,
executive, and judicial powers as well as the guarantee of human rights and the renunciation
of war except in self-defense. Japan's Government is composed of
a legislative branch called the Diet, an administrative branch which includes
the prime minister and his cabinet, and a judiciary branch.
Economy
Japan has
a gross national product of 2920 billion US dollars in 1989 second
only to the United States. A major factor in the success of the Japanese
economy has been the steady increase in productivity. In the years
1970-75, Japan's productivity rose by 33.3%, which was better than that
of other industrial nations. Despite Japan's rapid economic growth,
the country's standard of living is low when it is compared to the rest
of the world's industrial countries .
ENVIRONMENT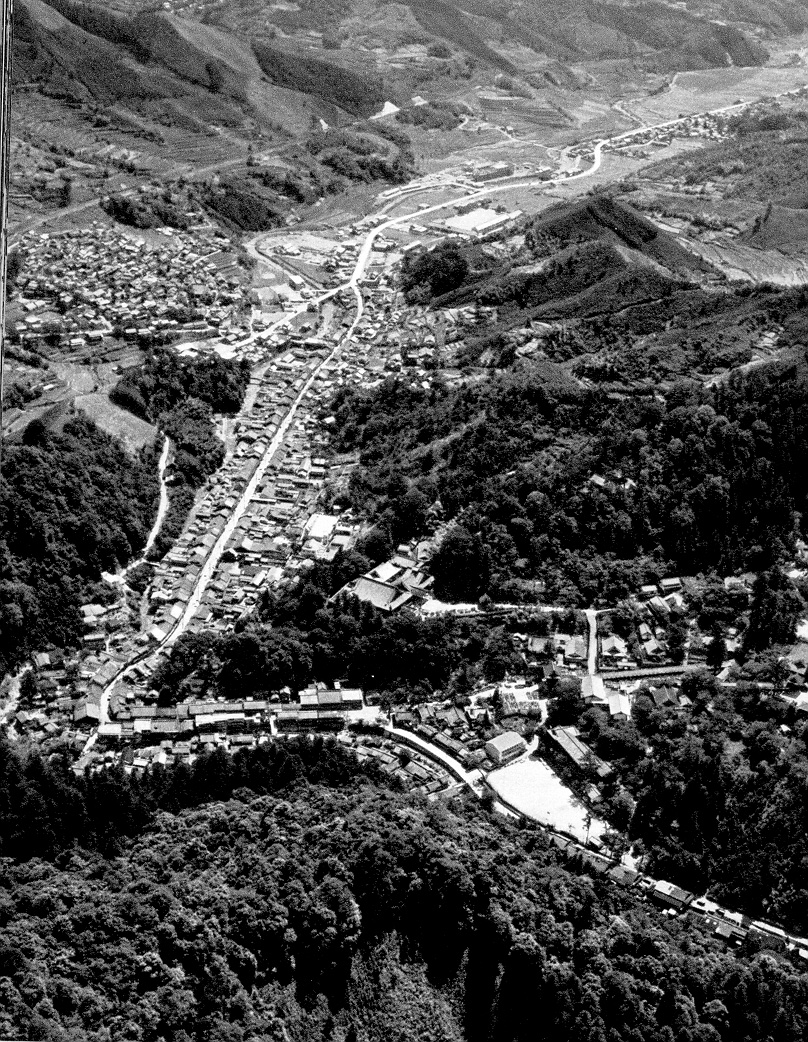
Geography
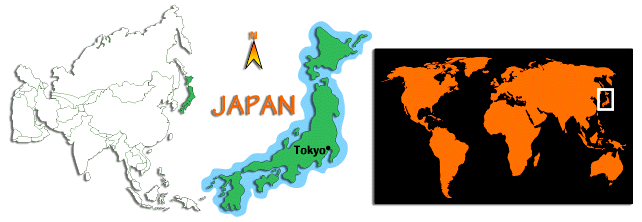
Japan
consists of a chain of islands off the east coast of the Eurasian land
mass extending in an arc north-east to south-west for a distance of 1735
miles. The average width of Japan is 145 miles. The main islands
that account for 97% of Japan's total land area, are Hokkaido in the north,
Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, lying opposite the Korean peninsula. The rest
of Japan's land area is made up of 3918 smaller islands, inlets and rocks,
some of which are very small and uninhabited. Japan is a country with 70% of its total
area occupied by wooded mountains and hills with 7%of
the area totally inaccessible; 11% consists of medowland and grazing;
while human settlement is confined to some 3% of the total area. The reason
for such a mountainous terrain is because Japan lies within the circum-Pacific
earthquake belt, and it is a relatively young land formation that is still
showing activity. Of its 285 volcanoes, 36 are still regarded as active,
although only 20 are recorded as having erupted since 1900. Japan's
great ranges of mountains leave little room for lowland areas, and in the
coastal areas there is usually only a narrow strip of land between the
foothills of the central highlands and the sea.
Climate
Japan has
four separate seasons comparable to that of Europe and North America. The
winter begins at almost the same time all over Japan, about the middle
of December. There is a big difference in temperature between northern
Japan, where winter brings severe cold, and south-western Japan where the
temperatures are above the freezing point all winter long. In mid February,
temperatures start to rise all over the county. In the southern part of
Japan, spring begins in March. May is pleasantly warm with temperatures
like that of a European summer. At the end of May, the main summer
rainy season starts. The rains begin earlier in the south where
they last longer and are more abundant. During this time, the wind has almost
stopped, the sky is overcast, the air is very humid, and the rain is fine
and penetrating. In the middle of July, the rain stops and tropical
air masses prevail all across Japan. The second half of July and August
tend to be the hottest months. Summer comes to an end in mid September. Autumn
comes in October bringing clear weather. The first snow falls in the
highlands of central Japan and winter begins in December once again.
TECHNOLOGY
Manufacturing
In 1945, Japanese production
of steel was about zero, by 1973, Japan's steel and iron production was a total
of 119 million tons making Japan one of the top steel manufactures in the
world. Many factors played a role in the growth of Japan's iron and
steel industry, including the rapid introduction of the latest technology,
huge investments in plants and facilities, and the expansion of the country's
domestic economy and export industries. Japan gets most of the iron ore
from Australia, Brazil, and India. Most of the coal comes from
Australia, the U.S., and Canada. Some of the other important fields
of production are motor vehicle manufacture( world leader of private cars),
shipbuilding, the manufacture of pharmaceuticals(world leader), paper,
optical apparatus, toys, entertainment electronics and electrical and computer
technology.
Research
Research is also
in progress on nuclear fusion. The main objective is the attainment of
an energy-break-even plasma condition required to create an experimental
fusion reactor. In 1985, the JT-60 was built, a testing device on
par with the United States fusion testing device. In August 1987, theJT-60
achieved the highest energy-break-even condition ever reached in the world
at that time. Other areas in which Japan is looking for new sources
of energy are coal liquefaction, thermal power generation, and solar batteries.
Research also continues on energy-saving technology.
This page was created by Michael Gonzalez as part of the
requirements for FCS428 International Housing in the Spring of 1998 at
California State University, Long Beach.
 ©1998
- This series of pages was developed in electronic form and made available
on-line by: Dr.
Lydia Sondhi, Family and Consumer Sciences, California State University,
Long Beach. ©1998
- This series of pages was developed in electronic form and made available
on-line by: Dr.
Lydia Sondhi, Family and Consumer Sciences, California State University,
Long Beach.
last updated: 06/02/98 |