Political Participation
III. Methods of Participation
- Conventional Participation: the use of established
institutions of representative government, especially campaigning
for candidates and voting in elections.
- voting, contributing money and working in
campaigns.
- writing letters to public officials, newspapers, and
companies.
- signing petitions, joining boycotts of advertisers.
- Unconventional Participation: challenges or defies established
institutions or the dominant culture.
- participating in strikes (usually by labor unions).
- demonstrations, picketing.
- non-violent civil disobedience.
- violence
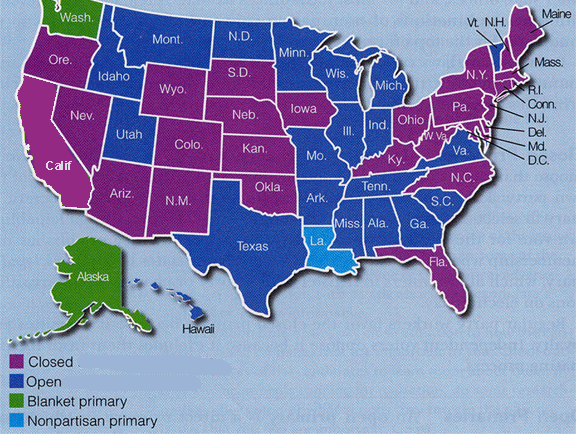
- Participation through Voting
- direct primary: an election used to nominate candidates
for the general election.
- closed
- open
- blanket
- non-partisan
- Types of Primary Elections in the States
- referendum: direct vote by the people
on either a law proposed or amendment to the state constitution.
In most states, referenda are usually placed on the ballot
by the legislature not voters.
- Propositions: The measure subject to popular
vote
- Initiative: a procedure (usually
circulating petitions) by which the people can propose an
issue to be decided by the legislalture or by the people in a
referendum.
