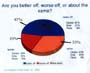
- The combined total of Democrats and Republicans far exceed the number of Independents.
- The percentage of Democrats normally exceeds the percentage of Republicans.
- There has been a gradual decline in the percentage of Democrats and Independents over the last 20 years.
- The percentage of Republicans has increased during the last 20 years.
- The percentage of Democrats, Republicans, and Independents have become nearly equal over the past 20 years.
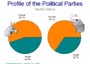
- The Distribution of Party Identification Among Young Voters, 1976 to 1993
- Independents are the largest group among young voters.
- For most of the period the proportion of Democrats was greater than the proportion of Republicans.
- From the mid 1980s to 1990, the percentage of Republicans among young voters exceed the percentage of Independents and the percentage of Democrats.
- By the mid 1990s, Independents are the largest single group in the electorate among younger voters
- The proportion of Democrats, Republicans, and Independents have become nearly equal.
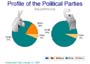
- The Distribution of Party Identifiers in California
- The Characteristics of Party Identifiers in the United States

[click on small graph to see a larger version of the graph]

1. Since 1932, socioeconomic factors (i.e., income, education, occupation) have distinguished Democrats and Republicans.
| Democrats | Republicans | |
| Income | lower to moderate | moderate to high |
| Education | high school grad or less;
post graduate degree |
some college;
collge degree |
| Occupation | blue collar union members; | managerial and clerical |



IV. American Voting Behavior
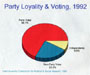
A. Party Loyality: Most voters choose candidates consistent with
their party identification
B. Evaluations of the voter's financial well being has a great
influence on voting behavior