AMERICAN FEDERALISM
Federalism: a system of government in which two or more
governments exercise power and authority over the same people
and the same territory.
I. Theories of Federalism
- Dual Federalism
- delegated or enumerated powers (Art. I, Sec. 8) restrict
functions of Federal govt.
- Federal government & states are sovereign within
jurisdiction
- relationship between the nation and the several
states is characterized by tension rather than cooperation.
- Cooperative Federalism:
- National, state, and local governments typically undertake government
fuctions jointly rather than exclusively.
- National government and states share power
- power is not concentrated at either level
- fragmentation of responsibilities gives people and groups access
to many centers of influence.
II. Constitutional Division of Powers
- Article I, Section 8:
Delegated or Enumerated powers exercised
exclusively by the Federal government
- McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
- "...the power to tax is the power to destroy."
- Implied Powers: derived from the "necessary and Proper clause"
(Article I, Section 8)
- Supremacy Clause (Article VI):
The Constitution, Treaties, and laws passed by Congress are
superior to state constitutions and state laws
- Reserved Powers (10th Amendment)
- powers reserved to the states (i.e., powers existing at time of
ratification).
- powers reserved to the people acting collectively or by
amending the Constitution.
III. Expansion of the National Government's Power
- National Emergencies
- Civil War: Defeat of States' Rights
- Great Depression: Expanded Economic Role
- Civil Rights Movement: Federal Protection of Individual Rights
over States' Rights
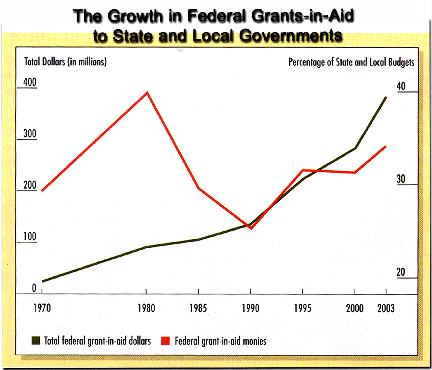
- Grant-in-Aids
- Adoption of Federal Income Tax as a Source of Revenue
(16th amendment)
- Massachusetts v. Mellon (1923): constitutionality of federal
grant-in-aids upheld (state action voluntary)
IV. Federalism Today (1937 to present): Inter-dependency and
Intergovernmental Relations
- Government Revenue
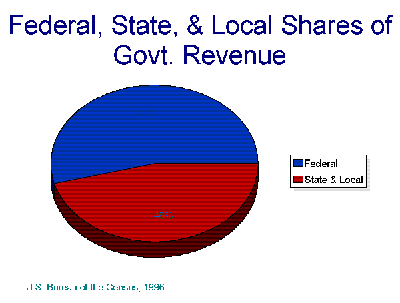
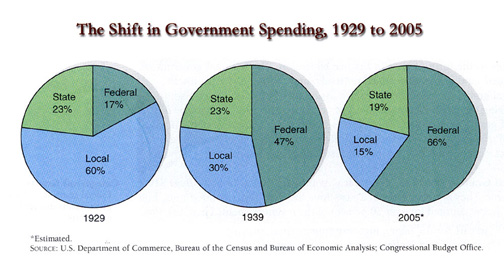
- Growth of Grant-in-Aids
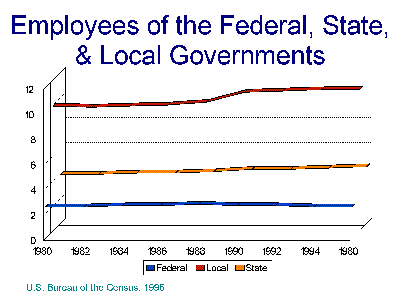
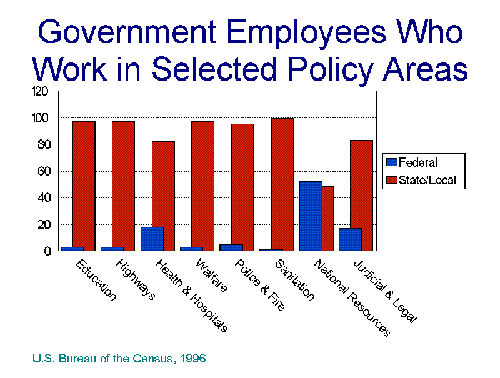
- Growth in Number of Government Employees
(Federal, State, and Local)
- Policy Areas: Federal/State/Local Responsibility
V. States Obligations to Each Other (Article IV)
Full Faith and Credit
- Marriage & Divorce (Same Sex Marriage)
- Financial Obligations
- Extradition








